The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as Black Tuesday, the Great Crash, or the Stock Market Crash of 1929, began on October 24, 1929, and was the most devastating stock market crash in the history of the United States. The crash signalled the beginning of the 12-year Great Depression that affected all Western industrialized countries.
The Roaring Twenties, the decade that followed World War I and led to the crash, was a time of wealth and excess. Building on post-war optimism, rural Americans migrated to the cities in vast numbers throughout the decade with the hopes of finding a more prosperous life in the ever-growing expansion of America's industrial sector.
The crash followed a speculative boom that had taken hold in the late 1920s. During the later half of the 1920s, steel production, building construction, retail turnover, automobiles registered, even railway receipts advanced from record to record. The combined net profits of 536 manufacturing and trading companies showed an increase, in fact for the first six months of 1929, of 36.6% over
1928, itself a record half-year. Iron and steel led the way with doubled gains. Such figures set up a crescendo of stock-exchange speculation which had led hundreds of thousands of Americans to invest heavily in the stock market. A significant number of them were borrowing money to buy more stocks. By August 1929, brokers were routinely lending small investors more than two-thirds of the face value of the stocks they were buying. Over $8.5 billion was out on loan, more than the entire amount of currency circulating in the United States at the time.
Despite the dangers of speculation, many believed that the stock market would continue to rise forever. On March 25, 1929, after the Federal Reserve warned of excessive speculation, a mini crash occurred as investors started to sell stocks at a rapid pace, exposing the market's shaky foundation. Two days later, banker Charles E. Mitchell announced his company the National City Bank would provide $25 million in credit to stop the market's slide. Mitchell's move brought a temporary halt to the financial crisis and call money declined from 20 to 8 percent.
However, the American economy showed ominous signs of trouble: steel production declined, construction was sluggish, automobile sales went down, and consumers were building up high debts because of easy credit. Despite all these economic trouble signs and the market breaks in March and May 1929, stocks resumed their advance in June and the gains continued almost unabated until early September 1929.

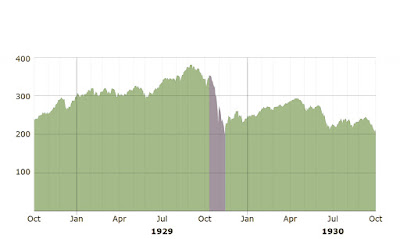
The market had been on a nine-year run that saw the Dow Jones Industrial Average increase in value tenfold, peaking at 381.17 on September 3, 1929. Shortly before the crash, economist Irving Fisher famously proclaimed, "Stock prices have reached what looks like a permanently high plateau." The optimism and financial gains of the great bull market were shaken after a well publicized early September prediction from financial expert Roger Babson that "a crash was coming". The initial September decline was thus called the "Babson Break" in the press. This was the start of the Great Crash, although until the severe phase of the crash in October, many investors regarded the September "Babson Break" as a "healthy correction" and buying opportunity.
On September 20, the London Stock Exchange crashed when top
British investor Clarence Hatry and many of his associates were jailed for fraud and forgery. The London crash greatly weakened the optimism of American investment in markets overseas. In the days leading up to the crash, the market was severely unstable. Periods of selling and high volumes were interspersed with brief periods of rising prices and recovery.
Selling intensified in mid-October. On October 24, the market lost 11 percent of its value at the opening bell on very heavy trading. The huge volume meant that the report of prices on the ticker tape in brokerage offices around the nation was hours late, so investors
had no idea what most stocks were actually trading for at that moment, increasing panic. Several leading Wall Street bankers met to find a solution to the panic and chaos on the trading floor. The meeting included Thomas W. Lamont, acting head of Morgan Bank; Albert Wiggin, head of the Chase National Bank; and Charles E. Mitchell, president of the National City Bank of New York. They chose Richard Whitney, vice president of the Exchange, to act on their behalf.
With the bankers' financial resources behind him, Whitney placed a bid to purchase a large block of shares in U.S. Steel at a price well above the current market. As traders watched, Whitney then placed similar bids on other "blue chip" stocks. This tactic was similar to one that ended the Panic of 1907. It succeeded in halting the slide. The Dow Jones Industrial Average recovered, closing with it down only 6.38 points for the day. The rally continued on Friday, October 25, and the half day session on Saturday the 26th but, unlike 1907, the respite was only temporary.
Over the weekend, the events were covered by the newspapers across the United States. On October 28, more investors facing margin calls decided to get out of the market, and the slide continued with a record loss in the Dow for the day of 38.33 points, or 13%.
The next day, October 29, 1929, about 16 million shares traded as the panic selling reached its peak. Some stocks actually had no buyers at any price that day. The Dow lost an additional 30 points, or 12 percent. The volume of stocks traded on October 29, 1929, was a record that was not broken for nearly 40 years.
On October 29, William C. Durant joined with members of the Rockefeller family and other financial giants to buy large quantities of stocks to demonstrate to the public their confidence in the market, but their efforts failed to stop the large decline in prices. Due to the massive volume of stocks traded that day, the ticker did not stop running until about 7:45 p.m.. The market had lost over $30 billion in the space of two days which included $14 billion on October 29 alone.
After a one-day recovery on October 30, where the Dow regained an additional 28.40 points, or 12 percent, to close at 258.47, the market continued to fall, arriving at an interim bottom on November 13, 1929, with the Dow closing at 198.60. The market then recovered for several months, starting on November 14, with the Dow gaining 18.59 points to close at 217.28, and reaching a secondary closing peak of 294.07 on April 17, 1930. The following year, the Dow embarked on another, much longer, steady slide from April 1931 to July 8, 1932, when it closed at 41.22—its lowest level of the 20th century, concluding an 89 percent loss rate for all of the market's stocks. For most of the 1930s, the Dow began slowly to regain the ground it lost during the 1929 crash and the three years following it, beginning on March 15, 1933, with the largest percentage increase of 15.34 percent, with the Dow Jones closing at 62.10, with an 8.26 point increase.

The largest percentage increases of the Dow Jones occurred during the early and mid-1930s. In late 1937, there was a sharp dip in the stock market, but prices held well above the 1932 lows. The market would not return to the peak closing of September 3, 1929, until November 23, 1954.